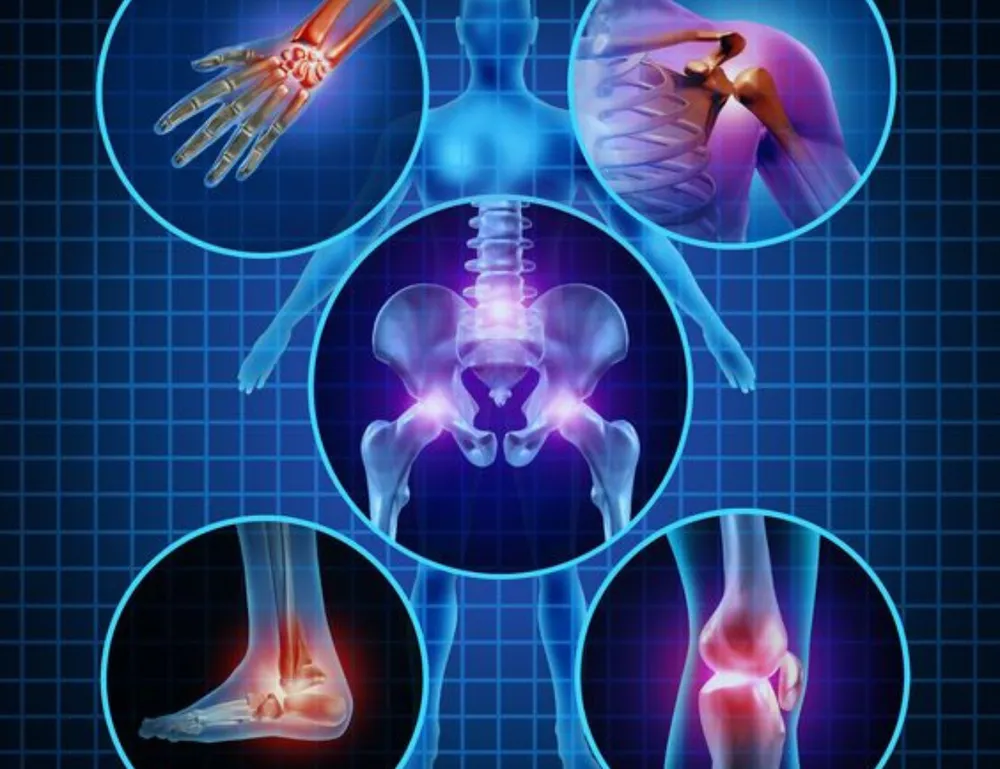
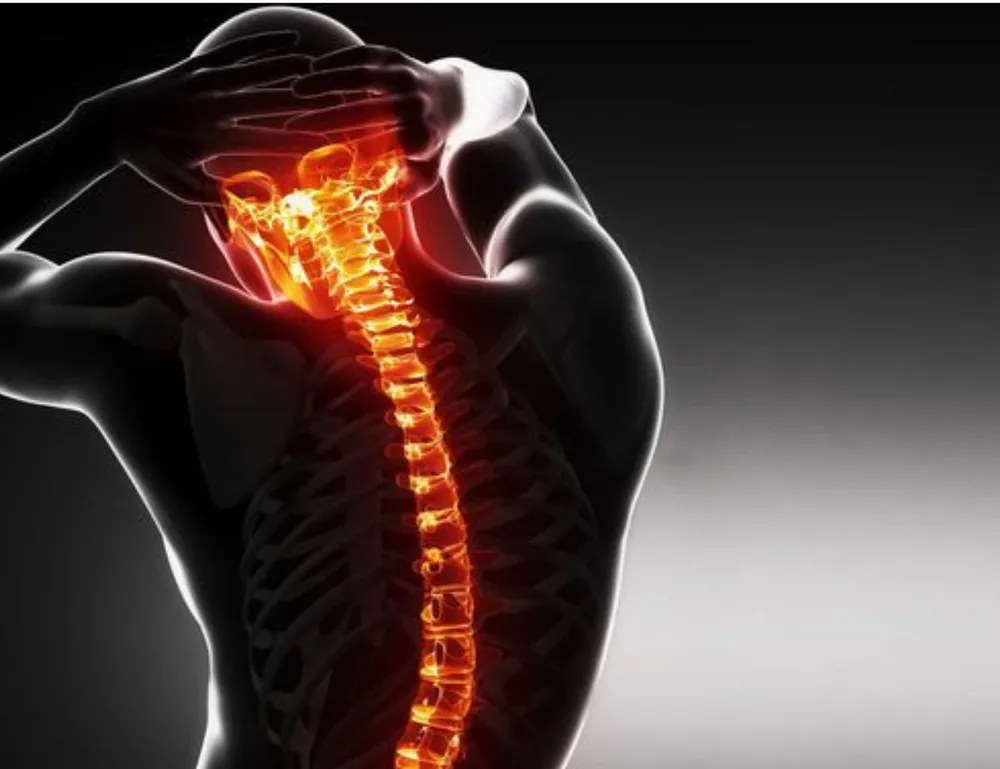

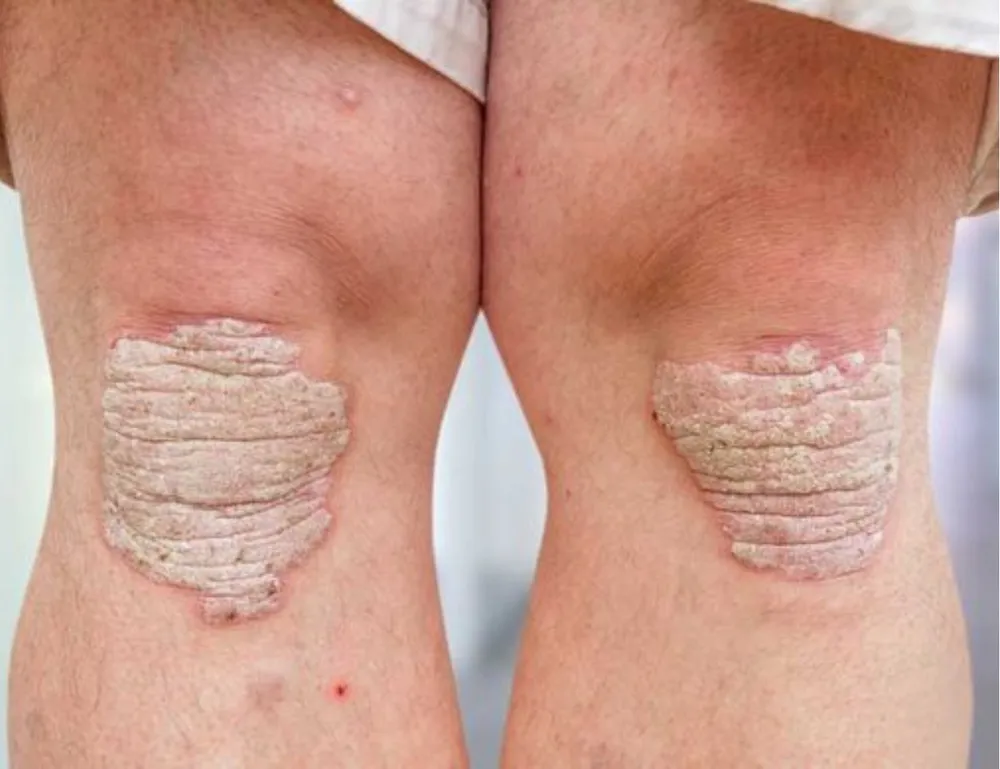
Genetics can influence the risk of developing rheumatic diseases in several ways. Certain genes have been identified as increasing the susceptibility to these conditions. For example, the HLA-DRB1 gene is strongly associated with rheumatoid arthritis, and variations in this gene can significantly increase the risk of developing the disease. Similarly, the HLA-B27 gene is linked to ankylosing spondylitis and other related conditions.
Genetic Factors in Rheumatic Diseases
- Immune System Regulation
Genes involved in immune system regulation can predispose individuals to autoimmune reactions. Variations in these genes can lead to an overactive immune response, attacking healthy tissues and leading to inflammation and pain characteristic of rheumatic diseases. - Inflammatory Pathways
Certain genetic markers influence inflammatory pathways in the body. These markers can enhance the production of inflammatory cytokines, proteins that play a crucial role in the inflammatory process. An imbalance in these cytokines can trigger chronic inflammation seen in rheumatic diseases. - Joint and Tissue Health
Genes affecting the health and integrity of joints and connective tissues can also contribute to rheumatic diseases. Mutations or variations in these genes can weaken these structures, making them more susceptible to damage and inflammation.
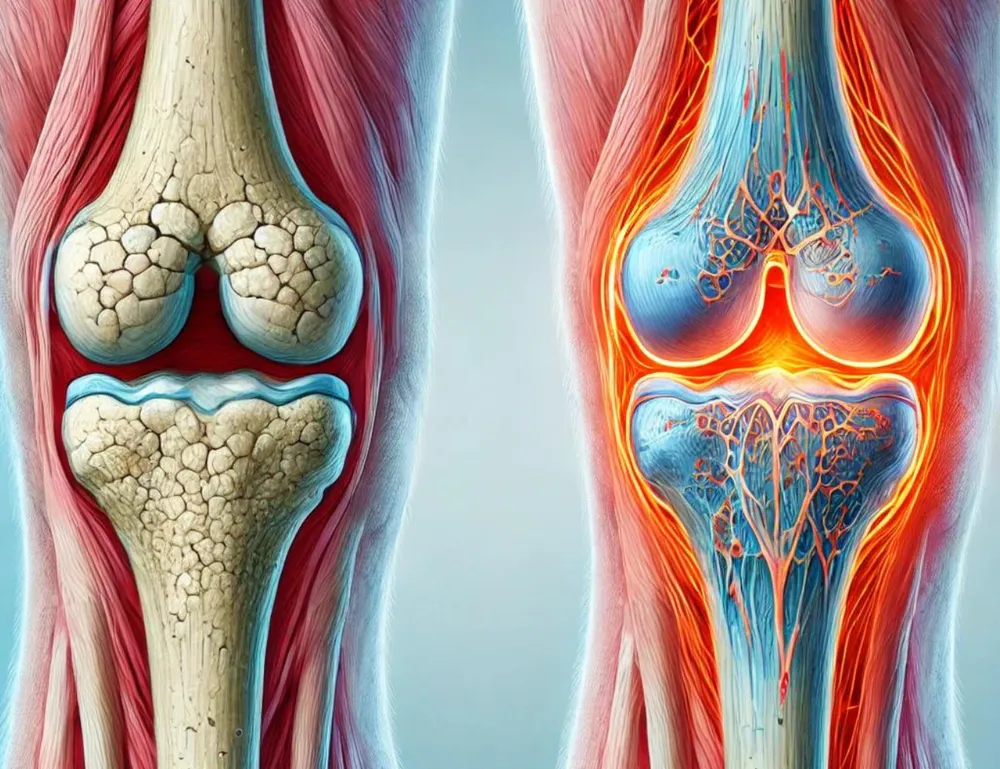
How Genetics Influence Rheumatic Diseases
If you have a family history of rheumatic diseases, you may be at a higher risk of developing these conditions. However, having genetic predispositions does not guarantee that you will develop a rheumatic disease. Environmental factors and lifestyle choices also play a critical role. Here are some steps to assess and manage your risk
- Family Medical History
Be aware of your family’s medical history. If close relatives have rheumatic diseases, discuss this with your healthcare provider. - Regular Check-Ups
Regular medical check-ups can help in early diagnosis and management of symptoms, preventing complications. - Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can reduce the risk of developing rheumatic diseases or manage symptoms effectively if you already have a genetic predisposition.



Are You at Risk?
Understanding the genetic factors in rheumatic diseases is crucial for early diagnosis, prevention, and personalized treatment. While you cannot change your genetic makeup, being aware of your risk and taking proactive measures can significantly impact your overall health and quality of life. If you have concerns about your risk for rheumatic diseases, consult with a healthcare provider for guidance tailored to your genetic profile and personal health history.