Introduction
Managing rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and osteoarthritis, involves a comprehensive approach that includes medication, lifestyle modifications, and supportive therapies. Among these, diet and exercise play crucial roles in alleviating symptoms, improving overall health, and enhancing quality of life. Here’s how diet and exercise can make a significant impact on managing rheumatic diseases.
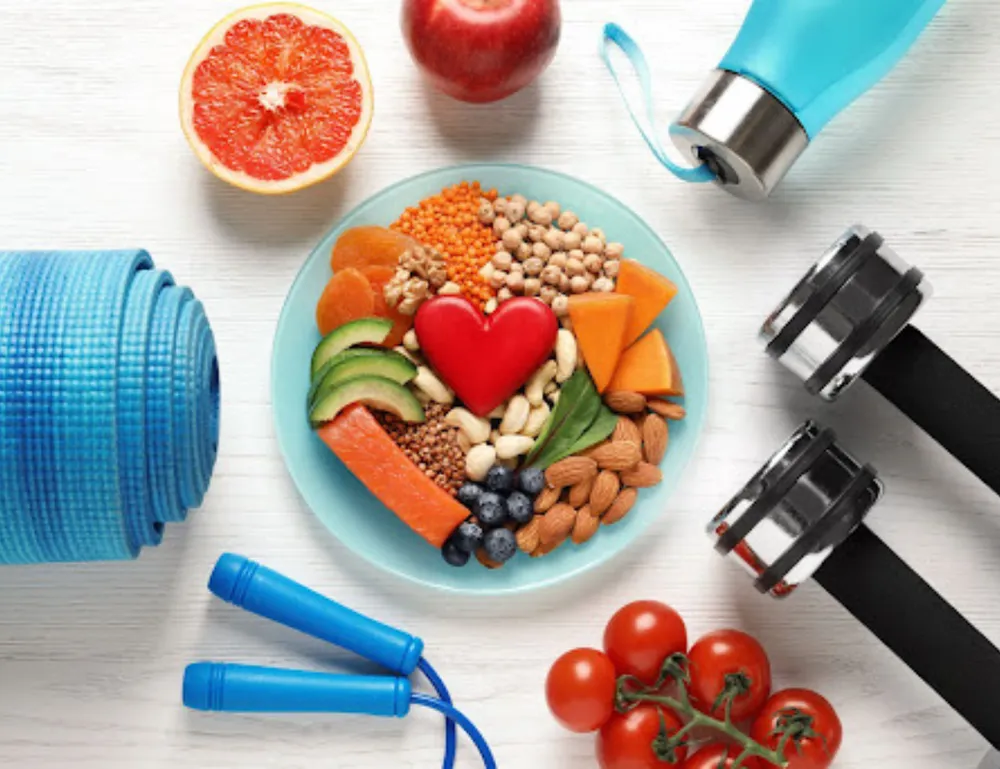

The Impact of Diet on Rheumatic Diseases
A well-balanced diet can help reduce inflammation, manage weight, and improve overall health, which are essential for managing rheumatic diseases.
Anti-Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods possess anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce the severity of symptoms in rheumatic diseases. These include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, they help fight inflammation and support overall health. Examples include berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and citrus fruits.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and other fatty fish are high in omega-3 fatty acids, which have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of healthy fats and anti-inflammatory compounds.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil contains oleocanthal, which has anti-inflammatory properties similar to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Foods to Avoid
Certain foods can exacerbate inflammation and should be limited or avoided:
- Processed Foods: These often contain unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives that can increase inflammation.
- Sugary Drinks and Snacks: High sugar intake can lead to increased inflammation and weight gain.
- Red and Processed Meats: These can contribute to inflammation and are often high in unhealthy fats.
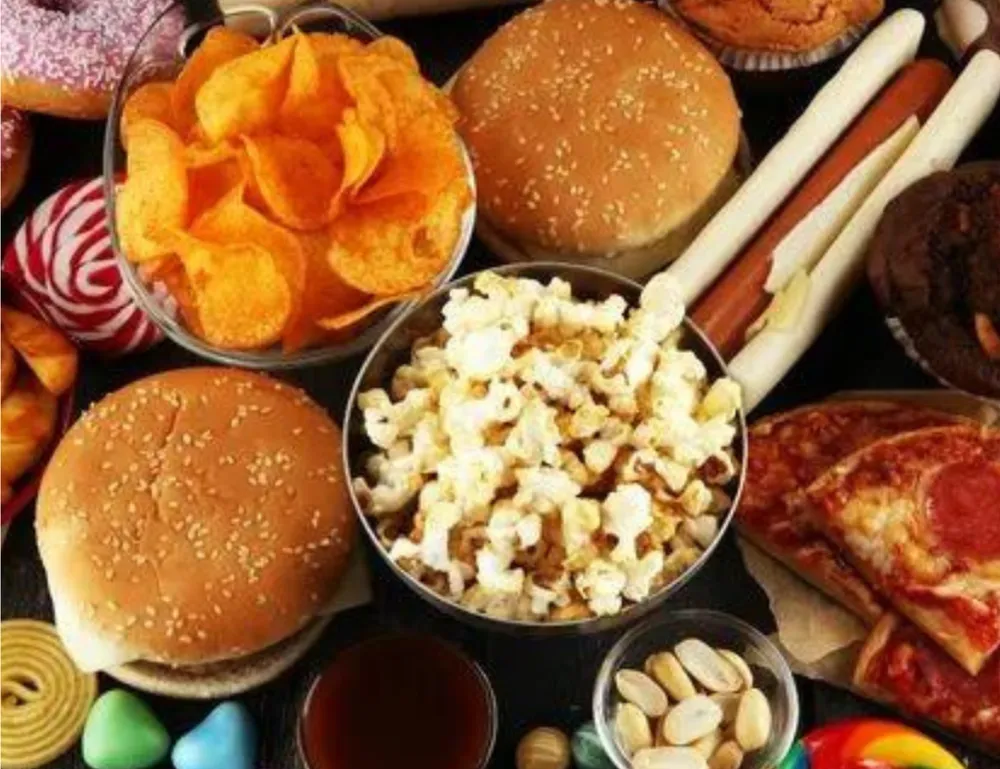

Processed Foods

Red and Processed Meats
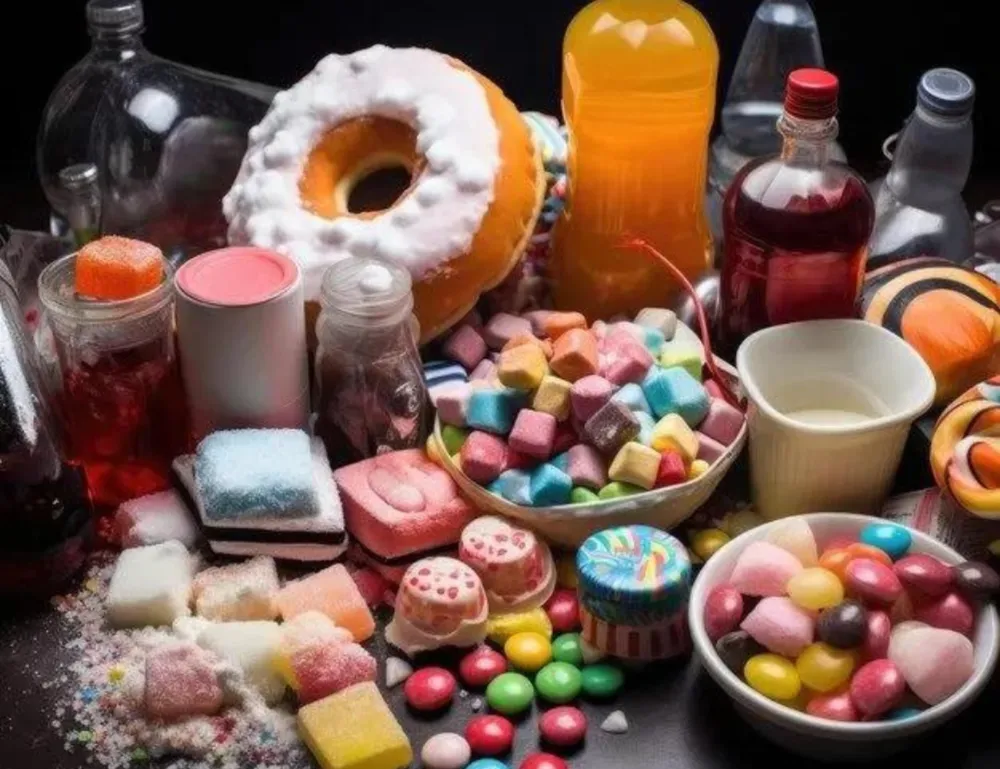

Sugary Drinks and Snacks
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Obesity can worsen symptoms of rheumatic diseases by putting additional stress on joints and increasing inflammation. A balanced diet can help maintain a healthy weight, thereby reducing strain on the joints and improving mobility.
The Role of Exercise in Managing Rheumatic Diseases
Regular physical activity is essential for managing rheumatic diseases. It helps improve joint function, reduce pain, and enhance overall physical and mental well-being.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling improve cardiovascular health and help manage weight. Swimming and water aerobics are particularly beneficial as they are low-impact and reduce stress on the joints.
- Strength Training: Building muscle strength can support and protect affected joints. Light weightlifting or resistance band exercises can be effective.
- Flexibility and Stretching Exercises: Yoga and stretching exercises improve flexibility, reduce stiffness, and enhance joint function. Tai chi is another excellent option that combines gentle movements with deep breathing and relaxation.
- Balance Exercises: Activities like yoga and tai chi also help improve balance, reducing the risk of falls and joint injuries.
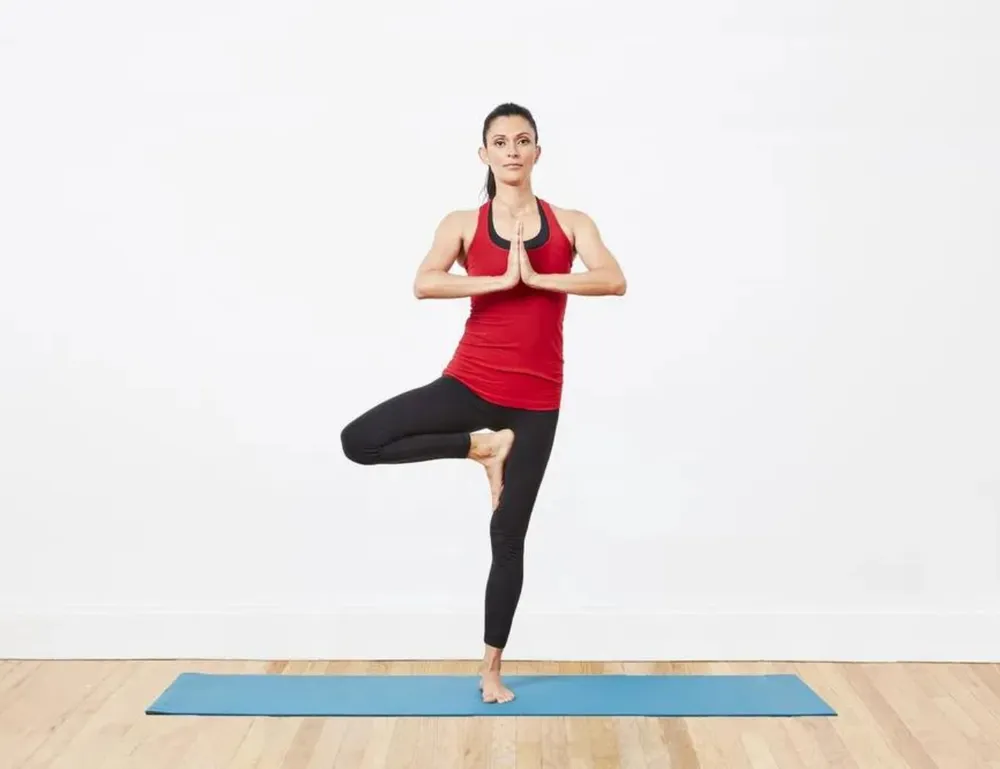

Aerobic Exercise

Strength Training

Flexibility and Stretching Exercises

Balance Exercises
Exercise Guidelines
- Consult Your Doctor: Before starting any new exercise regimen, consult with your healthcare provider to ensure it is safe and suitable for your condition.
- Start Slow: Begin with low-impact exercises and gradually increase intensity as your body adapts.
- Consistency is Key: Regular, moderate exercise is more beneficial than sporadic, intense workouts. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, along with strength training exercises on two or more days a week.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your body’s signals and avoid pushing through pain. Modify exercises as needed to prevent overexertion and injury.
Combining Diet and Exercise for Optimal Management
A combined approach of a healthy diet and regular exercise can significantly improve the management of rheumatic diseases.
Together, they help:
- Reduce Inflammation: Anti-inflammatory foods and regular physical activity both contribute to lower levels of inflammation in the body.
- Improve Mobility and Flexibility: Exercise helps maintain joint function and flexibility, while a balanced diet supports overall health and energy levels.
- Enhance Mood and Mental Health: Physical activity releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce feelings of pain and stress. A nutritious diet supports brain health and can help manage symptoms of depression and anxiety often associated with chronic diseases.
- Boost Immune Function: Both diet and exercise contribute to a stronger immune system, which is crucial for managing autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.

Reduce Inflammation

Improve Mobility and Flexibility
Enhance Mood and Mental Health
Boost Immune Function
Conclusion
Diet and exercise are integral components of managing rheumatic diseases. A well-balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, combined with regular physical activity, can help reduce symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life. Patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized diet and exercise plans that cater to their specific needs and limitations. By taking a proactive approach to diet and exercise, individuals with rheumatic diseases can take significant steps toward better health and well-being.