Introduction
Rheumatic diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, lupus, and fibromyalgia, can significantly impact a person’s ability to perform daily activities and maintain an independent lifestyle. Occupational therapy (OT) plays a crucial role in managing these conditions by helping patients adapt to their limitations, improve their functional abilities, and enhance their quality of life. Here’s an in-depth look at how occupational therapy contributes to the management of rheumatic diseases.
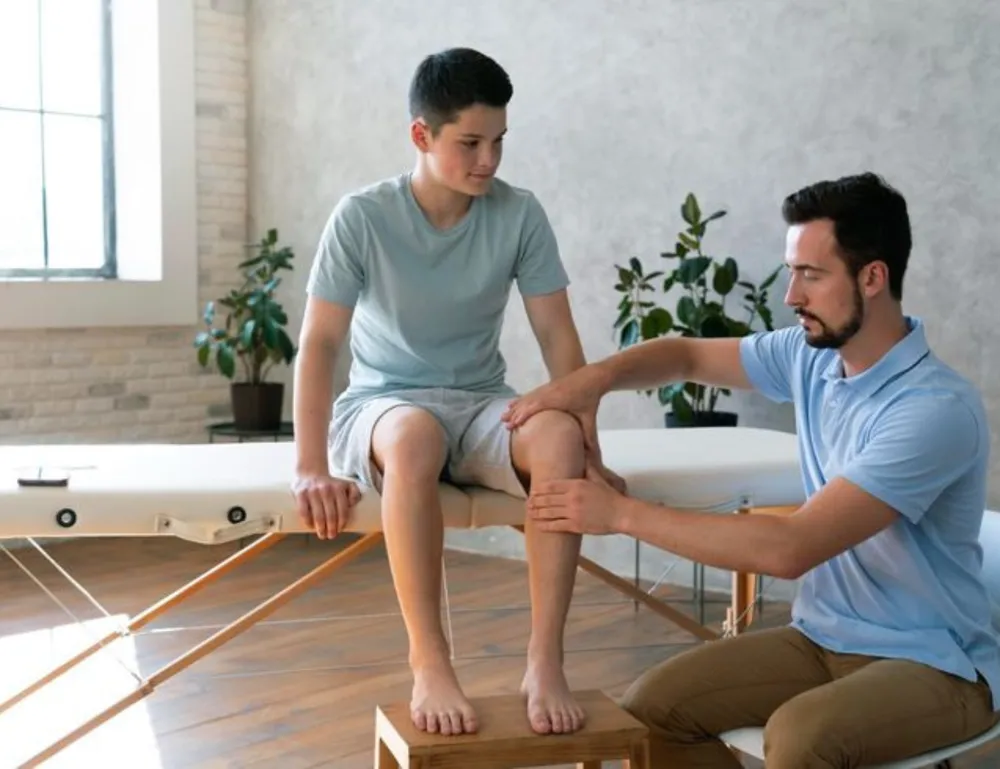

Understanding Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy is a healthcare profession that focuses on enabling people to participate in the activities of everyday life. Occupational therapists work with individuals of all ages who have physical, developmental, social, or emotional challenges that interfere with their ability to perform daily tasks.
Goals of Occupational Therapy in Rheumatic Disease Management
- Pain Management
- Therapeutic Techniques: Occupational therapists use various techniques, such as heat and cold therapy, massage, and gentle stretching, to help manage pain.
- Education: They educate patients about pain management strategies, including the use of assistive devices and adaptive techniques to reduce strain on affected joints.
- Improving Functional Abilities
- Exercise Programs: Customized exercise programs designed to improve strength, flexibility, and endurance without exacerbating symptoms.
- Joint Protection Techniques: Training in joint protection techniques to minimize stress on joints during daily activities. This includes using larger, stronger joints to carry loads and avoiding repetitive movements.
- Enhancing Mobility and Dexterity
- Adaptive Equipment: Recommendation and training in the use of adaptive equipment, such as reachers, dressing aids, and ergonomic tools, to assist with daily tasks.
- Splints and Orthotics: Designing and fitting splints or orthotic devices to support weakened joints and improve function.
- Energy Conservation
- Activity Modification: Teaching patients how to modify their activities to conserve energy and reduce fatigue. This might include pacing techniques, planning rest breaks, and prioritizing tasks.
- Work Simplification: Strategies to simplify work tasks, both at home and in the workplace, to make them more manageable.
- Improving Mental Health and Well-being
- Stress Management: Techniques to manage stress, anxiety, and depression, which are common in patients with chronic rheumatic diseases.
- Support and Counseling: Providing emotional support and counseling to help patients cope with the psychological impact of their condition.
Pain Management

Improving Functional Abilities

Enhancing Mobility and Dexterity

Energy Conservation

Improving Mental Health and Well-being
Practical Applications of Occupational Therapy
- Home Assessments
- Occupational therapists conduct home assessments to identify potential hazards and recommend modifications to make the home environment safer and more accessible. This can include installing grab bars, using non-slip mats, and rearranging furniture to allow for easier movement.
- Workplace Adaptations
- For patients who are employed, occupational therapists can suggest workplace adaptations to help them perform their job duties more comfortably and efficiently. This might involve ergonomic assessments and recommendations for adjustable chairs, desks, and computer equipment.
- Customized Treatment Plans
- Each patient receives a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs, goals, and lifestyle. This individualized approach ensures that the interventions are effective and relevant to the patient’s daily life.
- Education and Training
- Occupational therapists provide education and training to patients and their families about the nature of rheumatic diseases, self-care techniques, and the importance of adherence to treatment plans.

Home Assessments

Workplace Adaptations

Customized Treatment Plans

Education and Training
Success Stories
Many patients with rheumatic diseases have experienced significant improvements in their quality of life through occupational therapy.
For example:
- Case Study 1: A patient with severe rheumatoid arthritis was struggling with basic self-care tasks. With the help of an occupational therapist, they learned to use adaptive equipment for dressing and bathing, which increased their independence and reduced frustration.
- Case Study 2: An office worker with osteoarthritis received ergonomic assessments and modifications to their workstation, which alleviated joint pain and improved productivity.
Conclusion
Occupational therapy is a vital component of comprehensive rheumatic disease management. By addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of these conditions, occupational therapists help patients achieve greater independence, reduce pain, and enhance their overall well-being. If you or a loved one is living with a rheumatic disease, consider consulting an occupational therapist to explore the many ways they can support your journey to better health and improved quality of life.